Cactus Prizes and Major Achievements
Over the years, Cactus and its developers have won some of high performance computing’s most prestigious awards. Several are presented on this page.
-
Cactus Receives 2012 HPDC Award

A research paper whose co-authors include LSU’s Gabrielle Allen, Werner Benger, Andrew Merzky, and Ed Seidel has been named by the International ACM Symposium on High-Performance Parallel and Distributed Computing (HPDC) as one of the top 20 papers in the past 20 years of publications. HPDC is the premier computer science conference for presenting new research related to high-performance parallel and distributed systems used in both science and industry. Since its inception, HPDC has been at the center of new discoveries in systems such as clusters, grids, clouds, and parallel and multicore computers. -
IEEE Sidney Fernbach Award (2006)

Dr. Edward Seidel has been awarded one of the most prestigious awards for “outstanding contributions in the application of high performance computers using innovative approaches”. The IEEE computer society recognized Seidel for outstanding contributions to the development of software for high-performance computing and grid computing to enable the collaborative numerical investigation of complex problems in physics, particularly focusing on modeling black hole collisions.More information in the news story.
-
High-Performance Bandwidth Challenge (SC2002)

The LBNL/NCSA team has won the “Highest Performing Application” award at SuperComputing 2002 with the Cactus based application “Wide Area Distributed Simulations using Cactus, Globus and Visapult”. The wininig application transfers data at 16 GByte/s, modeling gravitational waves generated during the collision of black holes. -
High-Performance Computing Challenge Award (SC2002)

The Cactus team were a core part of the Global Grid Testbed Collaboration, who won both the “Most Geographically Distributed Application” and “Most Heterogeneous Set of Platforms” prizes at SC2002 for a task farming application written with Cactus which deployed Cactus Black Hole simulations across 70 diverse machines in 12 different countries. -
Gordon Bell Prize for Supercomputing (SC2001)

The Cactus team were a core part of the Global Grid Testbed Collaboration, who won both the “Most Geographically Distributed Application” and “Most Heterogeneous Set of Platforms” prizes at SC2002 for a task farming application written with Cactus which deployed Cactus Black Hole simulations across 70 diverse machines in 12 different countries. -
HPC “Most Stellar” Challenge Award (SC1998)
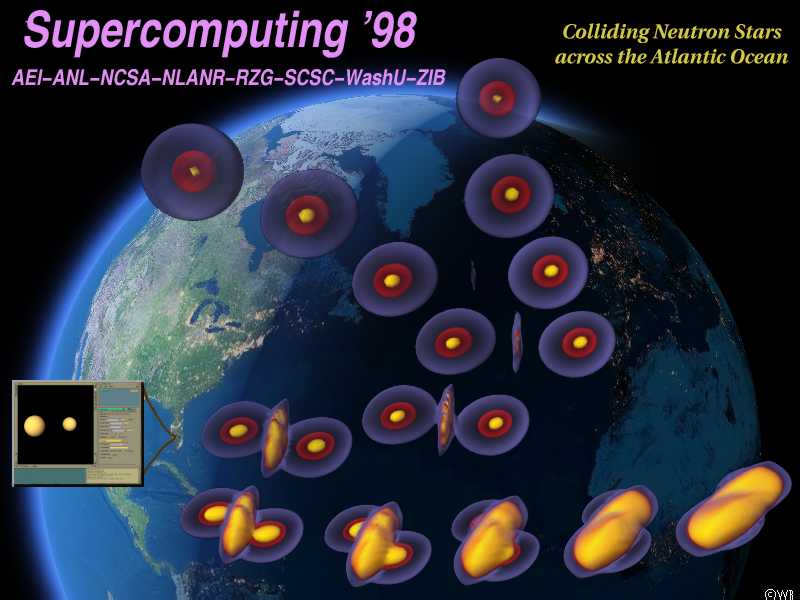
“Cactus 3.0” won the Most Stellar HPC Challenge Award at SC1998. The Cactus framework was used to perform a full three-dimensional simulation of colliding neutron stars based on Einstein’s equations. The simulation was distributed across two continents spanning the computational grid among three T3E’s in Garching (Germany), Berlin (Germany), and SDSC (United States). -
Heinz Billing Prize for Scientific Computing (1998)

The Heinz Billing Prize 1998 was awarded to Edward Seidel in recognition of his group’s work in scientific computing including the Cactus Code. This award is given by the Heinz Billing Society to promote scientific computing within the Max Planck Society.
